Efficient linear pumps are devices that are mainly used in water supply systems, hot water circulation systems, central heating systems, as well as systems designed for efficient water transport. Wherever efficient liquid transport is required, it is worth using reliable linear pumps. What should we pay attention to before choosing a linear pump? We have prepared a guide to facilitate the selection and installation of a linear pump in home, agricultural and industrial systems.
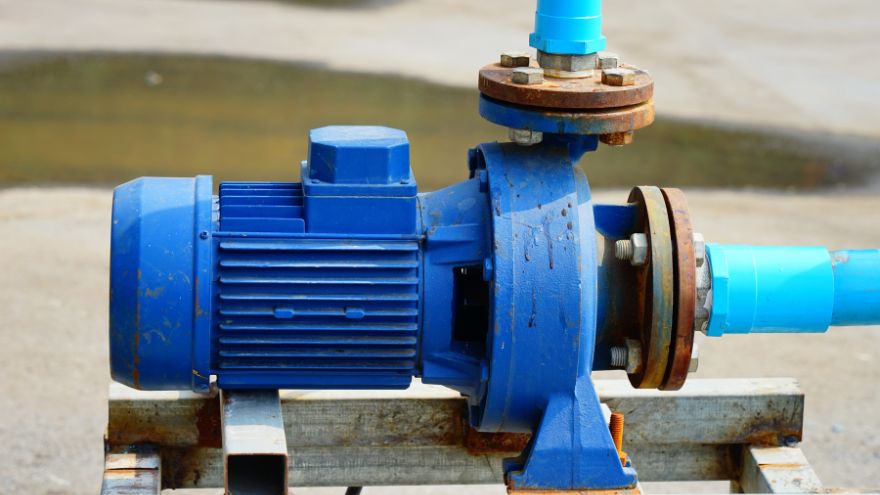

Check out the linear pumps at the Onninen wholesaler
What parts does a linear pump consist of?
The linear water pump is a fairly simple design. This is why linear pumps are efficient, energy-saving and reliable. The use of such water pumping devices causes the water to flow freely into the selected tank through the valve, and then it is pumped to further parts of the installation structure, e.g. water supply.
The basic structural elements of a water circulation pump are:
- Pump motor unit.
- Terminal box.
- Drive motor shaft.
- Split clutch.
- Coupler.
- Water pump shaft.
- Stuffing box, i.e. the BAQE system as a linear pump seal.
- Pump impeller.
- Body.
Water pumping devices connected to the installation, e.g. water supply, are also equipped with special seals, choke system and oil chambers, depending on the selected model. Each linear pump needs not only an efficient engine to operate effectively, but also a water pump shaft that can withstand even greater overloads.
Efficient linear pumps consist not of one hydraulic part, but of several, which include: single-stage centrifugal pumps, a dry rotor mounted on the shaft end, in-line housings and seals. The proper fit of all structural elements largely translates into how long the linear pump will operate efficiently.
The more durable the construction, the more efficient the pump will be at transporting water from one place to another.
In order for a linear pump to function efficiently for a long time of continuous use, it is necessary to protect the housing well against water penetration onto individual mechanical parts. In this case, manufacturers use BAQE seals.
How to match the power of a linear pump to the needs of the installation?
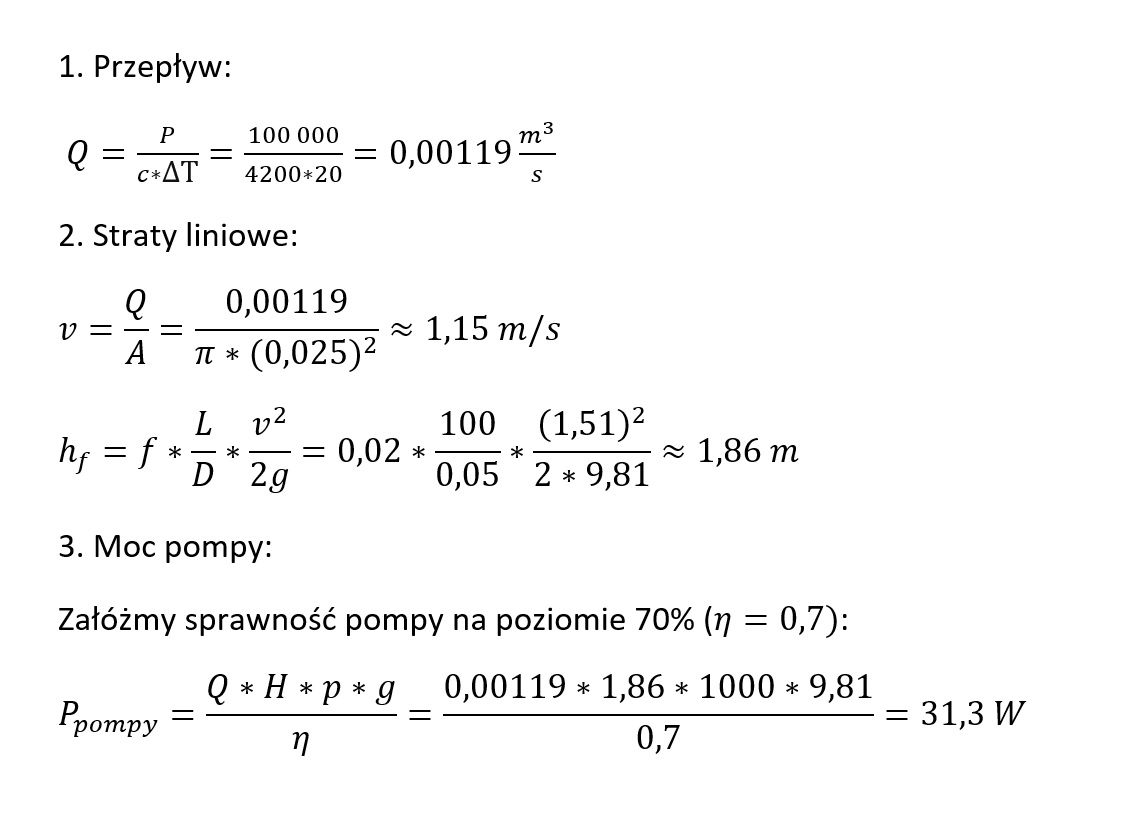
When selecting the power of a linear pump to meet the needs of, for example, a water supply system, we should consider not only the basic technical parameters of the pump, but also the demand for liquid flow efficiency. We should also remember that a higher pump power requires a suitably stable power supply. Only then can the device operate at maximum efficiency declared by the manufacturer. In this case, we use simple mathematical formulas.
Fluid flow
It allows you to determine the amount of liquid that a linear pump must pump in a given unit of time. The calculations in this case are as follows:
- Q – flow (m³/s)
- P – thermal power of the installation (W)
- c – specific heat of the liquid
- ΔT – temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the installation (K)
To determine the fluid flow, we divide the thermal power of the installation by the product of the specific heat and the temperature difference.
Pressure
The second important parameter needed to finally determine the demand for linear pump power is pressure (lifting height). In this case, the result depends on linear losses due to resistance in pipelines, as well as local losses, e.g. on valves and elbows.
To calculate the exact pressure losses, we need to use the Darcy-Weisbach formula, taking into account:
- h1 – pressure loss (m)
- f – friction coefficient (depends on the type of pipe and flow)
- L – pipe length (m)
- D – pipe diameter (m)
- v – flow velocity (m/s)
- g – gravitational acceleration (9.81 m/s²)
To perform the calculations, we multiply the friction coefficient by the ratio of the pipe length to the diameter. The result is multiplied by the ratio of the flow velocity squared to the double gravitational acceleration.
Linear pump power
To calculate the power of a rope pump, we need calculations related to the flow and pressure of water in the installation. To estimate the optimal pump power in Watts, we need to prepare the following data:
- Q – flow (m³/s)
- H – lifting height (m)
- ρ – density of the liquid (for water ρ≈1000 kg/m³ρ≈1000kg/m³)
- g – gravitational acceleration (9.81 m/s²)
- η – pump efficiency (coefficient, e.g. 0.7 for 70% efficiency)
Assuming that the heating system has a power of 100 kW and the temperature difference is 20 degrees Celsius with a pipeline length of 100 m, the optimal power of the linear pump will be around 3-4 kW.
What kind of motor should a linear pump have?
The optimal motor for linear pumps operating at higher pressure should be single-phase or three-phase. The ideal choice is an air-cooled, constant-speed unit, which ensures uniform water flow throughout the entire time the linear pump is operating.
Additionally, an efficient and reliable linear pump motor should be:
- powered by a maximum voltage of 400V (optimally 230V),
- composed of a motor and pump shaft connected by a rigid sleeve coupling,
- 100% closed and protected against water penetration into individual structural elements.
The most popular solution used in pumps for forcing water circulation is a dry engine rotor. In addition, a body made of GG 25 cast iron, stainless steel or cast steel will be an ideal combination that guarantees reliability and efficient operation in all conditions.
What protection class should a linear pump have?
 According to IEC standards, the insulation class against hazardous input voltage levels should have a factor F, i.e. a maximum winding temperature of 155 degrees Celsius with a thermal margin of up to 10 degrees.
According to IEC standards, the insulation class against hazardous input voltage levels should have a factor F, i.e. a maximum winding temperature of 155 degrees Celsius with a thermal margin of up to 10 degrees.
Linear pumps for use in water environments should also be insulated according to IP standards. Modern pumping units are most often made in the safety class:
- IP54 – resistant to drops falling at any angle from all sides (rain) and dust-proof.
- IP 55 – almost 100% dust-proof and full protection against moisture.
A great example of an efficient and perfectly insulated linear pump is the model: Grundfos IN-LINE linear pump with a dry rotor motor TP150-220/4-AFA-GQQE . This pump is coated with a corrosion protection coating, enabling operation at temperatures up to 60 degrees Celsius with a power output of 18.5 kW.
Check out the linear pumps at the Onninen wholesaler
What RPM range should a linear pump have?
 The rotational speed of the linear pump, or more precisely the impeller driving the water circulation, should be adapted to the conditions in which the pump will be used. Models available in our wholesale offer are available in versions with rotational speeds from 1400 RPM to 2950 RPM per minute. The most popular linear pumps are those with speeds of 2900 RPM/min. and 1450 RPM/min.
The rotational speed of the linear pump, or more precisely the impeller driving the water circulation, should be adapted to the conditions in which the pump will be used. Models available in our wholesale offer are available in versions with rotational speeds from 1400 RPM to 2950 RPM per minute. The most popular linear pumps are those with speeds of 2900 RPM/min. and 1450 RPM/min.
Remember that the selection of the pump in terms of the speed range is one of the most important factors affecting the efficiency of the device.
The Grundfos IN-LINE dry rotor linear pump model TP 50-190/2-AFA-GQQE is a good example of a pump with an optimal speed range that combines low energy consumption and efficiency. The In-line system in this model is equipped with a quiet motor in the efficiency class IE3.
What is the BAQE standard linear pump seal?
The standard sealing of pumps in hot water circulation systems, central heating installations or even for pumping clean liquids is the so-called BAQE system:
- B – shaft seal with rubber bellows.
- A – sealing of rotating belemnites with carbon that is impregnated with antimony.
- Q – sealing of fixed elements of the linear pump with the help of silicon carbide.
- E – secondary seal EDPM (ethylene-propylene-diene rubber).
This form of sealing the pump and hydraulic parts inside the housing is a guarantee of effective and failure-free operation of the device for many years of use. Additionally, the BAQE system translates into the absence of the need for human operation of the pump - once connected, it can function efficiently for a long time, e.g. in refrigeration systems.
A slightly more powerful 4 kW model of the Grundfos IN-LINE dry rotor pump TP80-210/2-AFA-BAQE , in which the complete BAQE protections have been implemented. Thanks to this, there is no risk of the unit being damaged or failing due to water leaks into the unit.
Our offer also includes many other products designed for pumping water in various places. We also offer submersible pumps, deep well pumps and many other devices for use in industrial installations and air conditioning systems. The available submersible pumps ensure that the water drawn has the right pressure - of course, assuming that the equipment has the right power consumption and the geometric height of the installation does not exceed the manufacturer's recommendations.
Where are linear pumps used?
The application of the linear pump and submersible pumps is not only private buildings, but also commercial ones. Vertical pumps in the In-line system are suitable for water supply installations, air conditioning installations, farms, as well as for forcing water circulation in commercial buildings.
The popularity of this type of pumping units is due to several advantages of linear pumps, which include:
- low electricity consumption,
- low installation and operating costs,
- long-term and failure-free operation even in difficult conditions,
- no need for maintenance,
- high efficiency of dry rotor motors.
When choosing linear pumps for specific applications, we should carefully analyze all technical parameters, water insulation class, and also review the most popular models on the market. In our wholesale offer you will easily find linear pumps for central heating, cooling systems and installations that work with higher liquid pressure.