When planning to build a house or renovate a building, we choose innovative solutions such as carbon monoxide, gas or smoke detectors. By equipping your home with, for example, a smoke detector, you significantly increase your safety. Therefore, it is worth equipping your home with smoke, gas or carbon monoxide detectors to detect dangers. A smoke sensor protects against fire, a carbon monoxide detector against carbon monoxide poisoning, and a natural gas sensor warns against gas leaks. But what exactly is the difference?
Check the danger sensors at the Onninen wholesaler
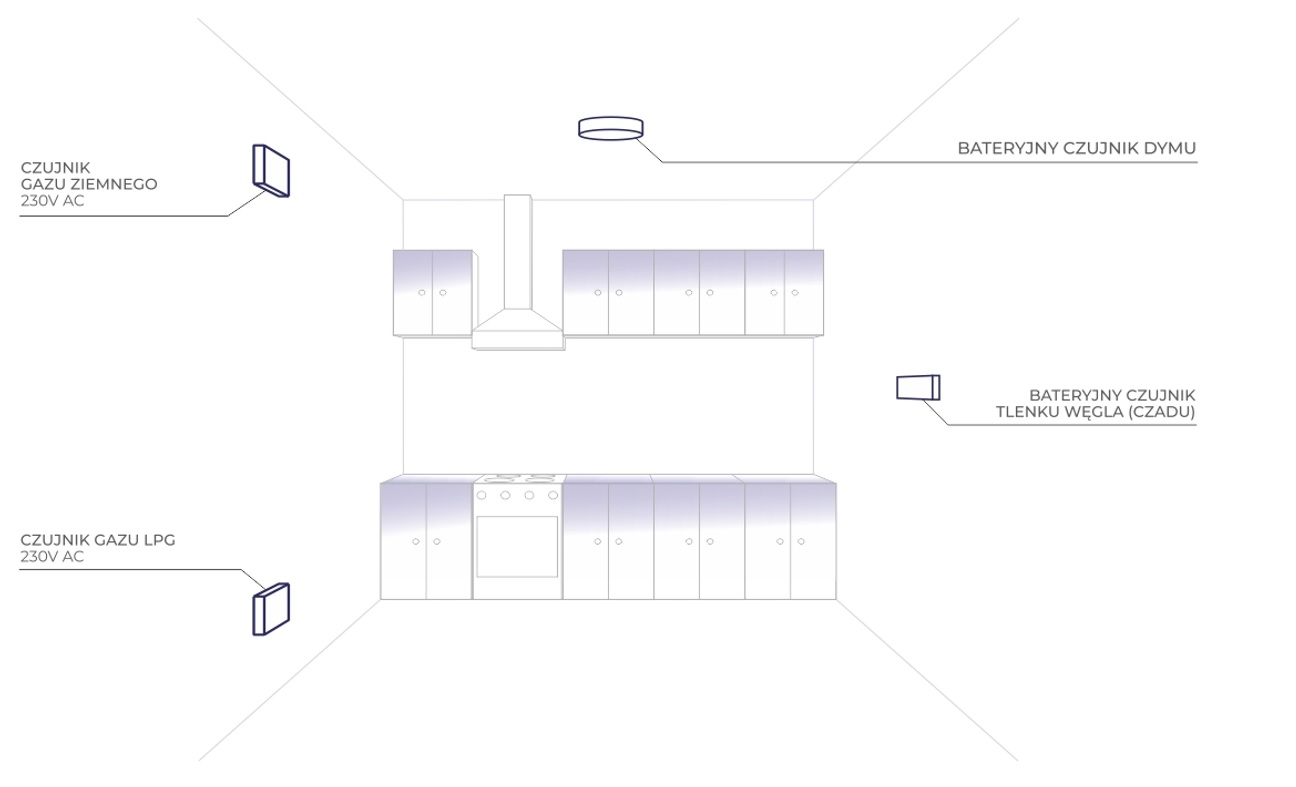
Where to install a smoke detector?
A properly installed smoke detector should be located in the center of the room's ceiling. Away from a fan, door or window that will blow in potential hazards and prevent the smoke detector from detecting them.
During the combustion process or even initial ignition, smoke is produced. The source of smoke may be burnt dinner, smoldering, faulty electrical installation, or an open fireplace or stove. Its quick detection allows for immediate reaction and possible summoning of help before a fire breaks out and consumes our entire house. This can be prevented by installing a smoke detector.
Sensor mounting diagram
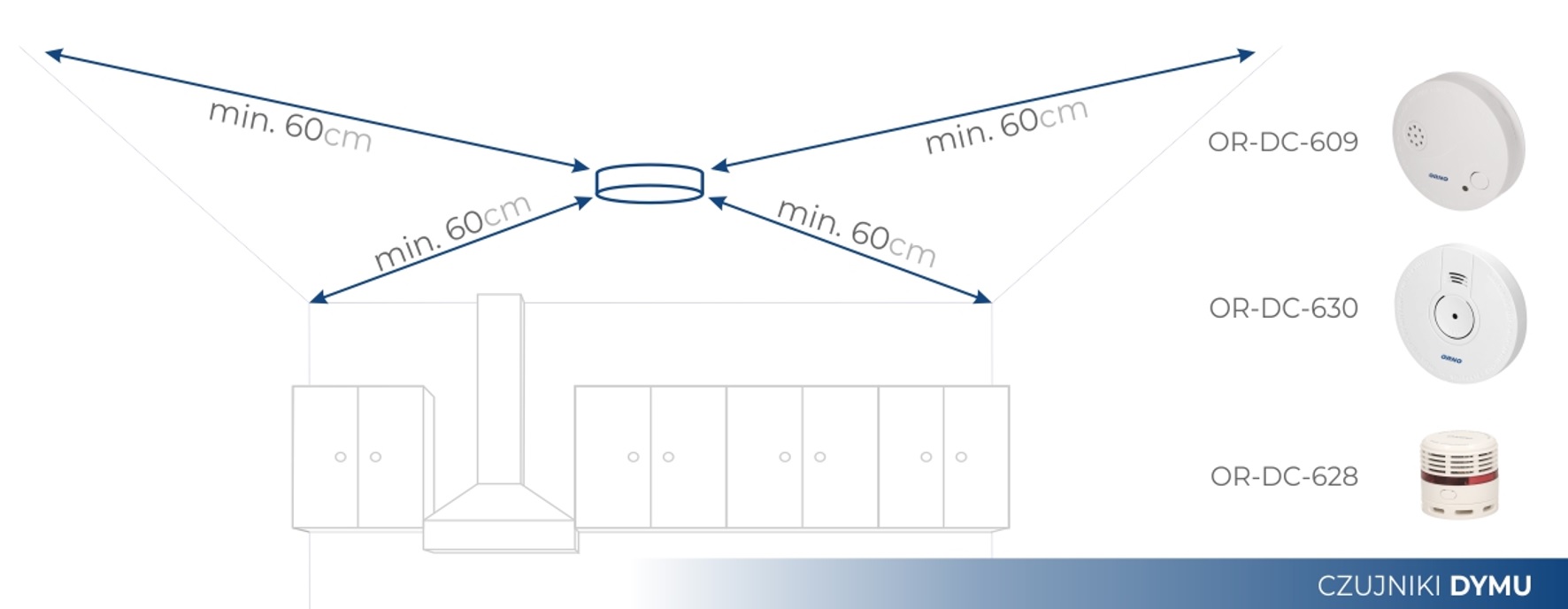 Smoke detector installation diagram
Smoke detector installation diagram
How is carbon monoxide produced?
Carbon monoxide gas occurs as a result of incomplete ventilation and aeration of the room when it is ineffective. Carbon monoxide accumulates, especially when air vents are intentionally sealed. Carbon monoxide gas may be produced by a faulty gas instantaneous water heater or may even be blown into the room through the chimney.
A potential source of carbon monoxide is a stove or fireplace, where the lack of a sufficient amount of supplied air causes the above-mentioned incomplete combustion. A carbon monoxide detector mounted at eye level in the most frequently used room allows you to objectively assess the amount of CO particles in the inhaled air. Installing a smoke and carbon monoxide detector on the ceiling in one device leads to incorrect readings, because even a 100% efficient ventilation system is not able to immediately remove the naturally occurring carbon monoxide in quantities that do not pose a threat to health.
Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning
CO concentration in air ppm* | Inhalation time (approximate) and development of symptoms |
| 50 | Maximum permissible concentration for continuous exposure for a period of 8 hours. |
| 150 | Slight headache after 1.5 hours. |
| 200 | Slight headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea after 2-3 hours. |
| 400 | Pain in the front of the head within 1-2 hours. Life-threatening after 3 hours |
| 800 | Dizziness, nausea and convulsions within 45 minutes. Loss of consciousness within 2 hours Death within 2-3 hours. |
| 1600 | Headache, dizziness and nausea within 20 minutes. Death within 1 hour |
| 3200 | Headache, dizziness and nausea within 5-10 minutes. Death within 25-30 minutes. |
| 6400 | Headache, dizziness and nausea within 1-2 minutes. Death within 10-15 minutes. |
| 12800 | Death within 1-3 minutes. |
*The ppm unit indicates the concentration of the (poisonous) gas.
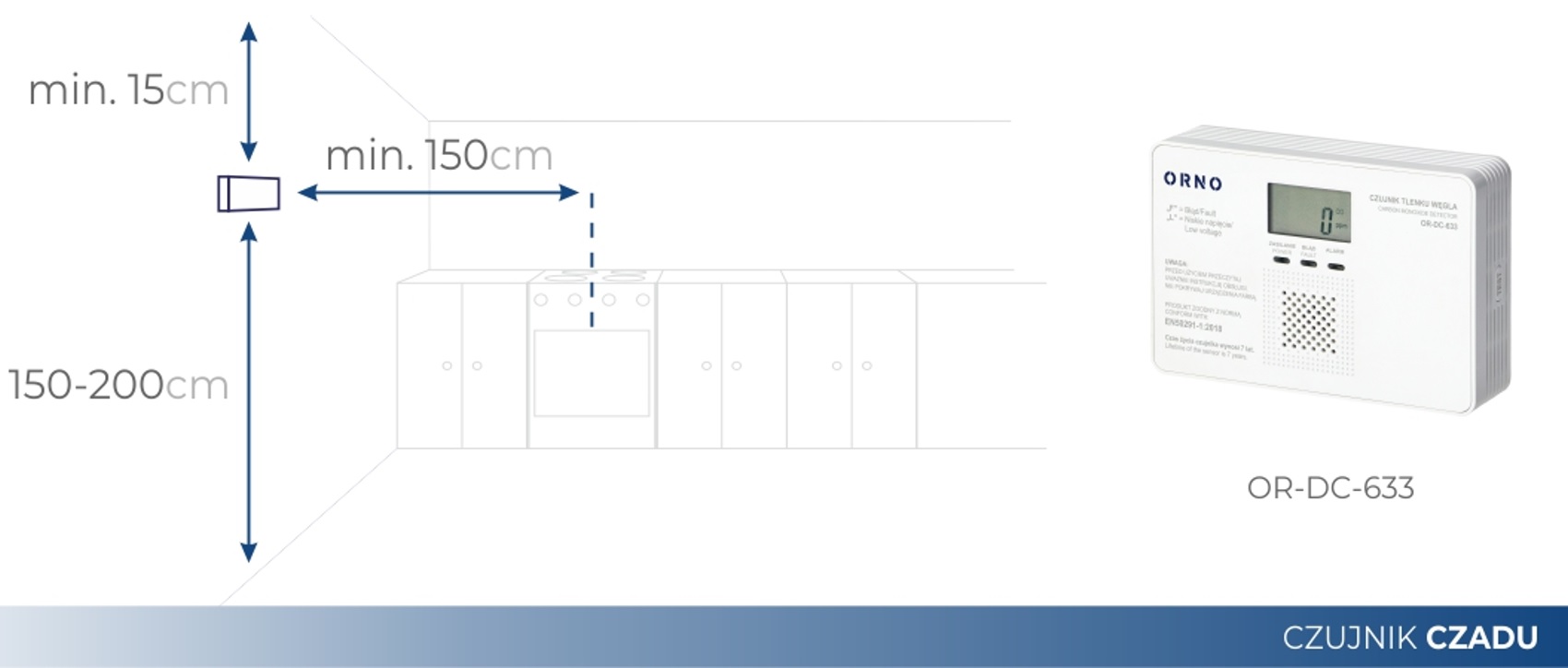 Installation diagram of the carbon monoxide sensor
Installation diagram of the carbon monoxide sensor
Check the danger sensors at the Onninen wholesaler
Where to install the gas sensor and natural gas sensor?
 To properly discuss the topic, it should be noted that methane is natural gas supplied from the installation, and the propane-butane mixture, i.e. LPG gas, comes from the cylinder. The first one is lighter than air and the natural gas sensor monitoring its concentration is mounted near the ceiling, while the gas sensor has a very high density and accumulates near the floor. Gases mixing with air create an explosive mixture, and one spark from even a light switch is enough to initiate a deadly explosion.
To properly discuss the topic, it should be noted that methane is natural gas supplied from the installation, and the propane-butane mixture, i.e. LPG gas, comes from the cylinder. The first one is lighter than air and the natural gas sensor monitoring its concentration is mounted near the ceiling, while the gas sensor has a very high density and accumulates near the floor. Gases mixing with air create an explosive mixture, and one spark from even a light switch is enough to initiate a deadly explosion.
Due to the fact that both gases have different structures and calorific values, they cannot be detected correctly with a "universal" sensor. The use of such a common sensor will lead to false alarms, or worse still, no alarms at all. Two sensors are needed for full protection: a gas sensor and a natural gas sensor.
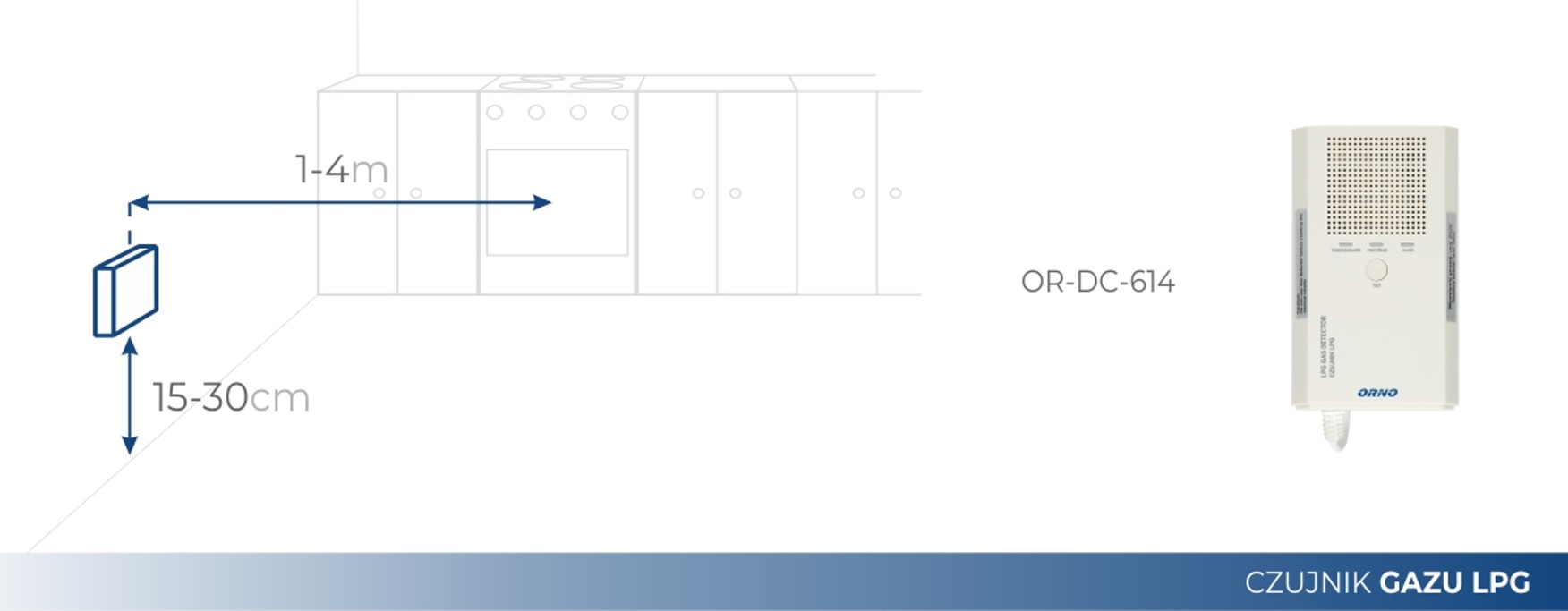
LPG gas sensor installation diagram
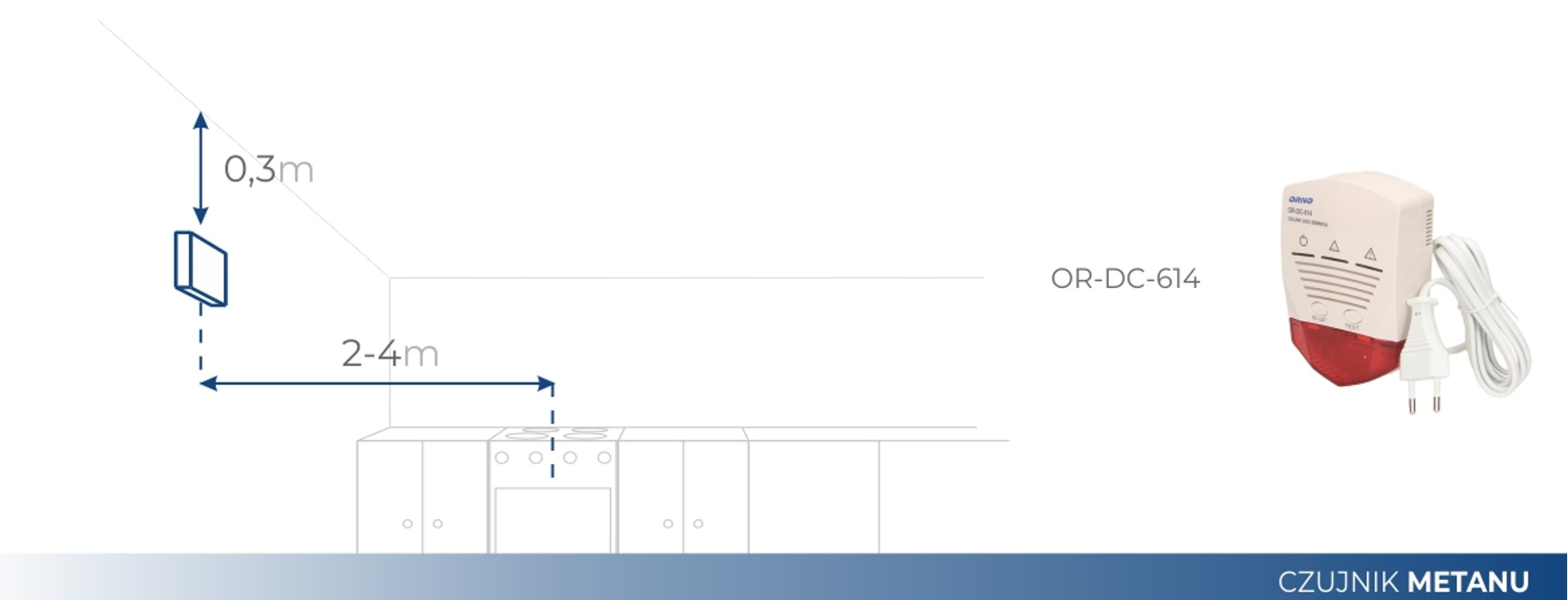
Gas sensor/methane sensor installation diagram
You should be especially careful about the so-called “magic” devices that detect everything at once. One sensor on the ceiling will never detect all threats or will alert about them even though there is no immediate threat.
Where should carbon monoxide detectors, smoke detectors, gas detectors and natural gas sensors not be installed?
- Too close to windows, doors and grates
 ventilation: Mounting sensors, e.g. carbon monoxide detectors, too close to windows, doors or ventilation grilles may affect their operation. The proximity of these elements may lead to signal interference, affecting the accuracy of sensor readings. To ensure proper operation of the sensors, it is recommended to install them in places that are not directly exposed to the influence of air flow from these sources.
ventilation: Mounting sensors, e.g. carbon monoxide detectors, too close to windows, doors or ventilation grilles may affect their operation. The proximity of these elements may lead to signal interference, affecting the accuracy of sensor readings. To ensure proper operation of the sensors, it is recommended to install them in places that are not directly exposed to the influence of air flow from these sources. - In the air stream of mechanical ventilation or air conditioning: Sensors, e.g. smoke detectors, should not be installed in the direct stream of air leaving mechanical ventilation or air conditioning systems. Strong airflow may distort the readings of smoke detectors or cause their operation to become unstable. It is important to place smoke detectors in places where the air flow is even and unobstructed.
- Directly above the gas stove,
 stove or fireplace (minimum distance 150cm): Installing sensors, e.g. gas sensors, directly above a gas stove, stove or fireplace may lead to incorrect readings and compromise safety. Due to the potential source of heat, fire or gas emissions, it is recommended to maintain a minimum distance of 150 cm between these devices and gas sensors.
stove or fireplace (minimum distance 150cm): Installing sensors, e.g. gas sensors, directly above a gas stove, stove or fireplace may lead to incorrect readings and compromise safety. Due to the potential source of heat, fire or gas emissions, it is recommended to maintain a minimum distance of 150 cm between these devices and gas sensors. - At a height that is not suitable for the given sensor: Each type of sensor, for example a natural gas sensor, has a specific installation height, which depends on its purpose and technical specifications. It is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the appropriate installation height. Installing natural gas sensors at an inappropriate height may lead to incorrect readings and loss of sensor functionality, resulting in loss of safety.
Remember that proper installation of sensors is crucial to ensure proper operation and accurate readings. It is always a good idea to consult your sensor manual or use the services of a professional to ensure that your sensors are placed in the correct locations.
